AdTech specializes in the research and production of aluminium refining fluxes used in the aluminum casting industry for more than ten years.
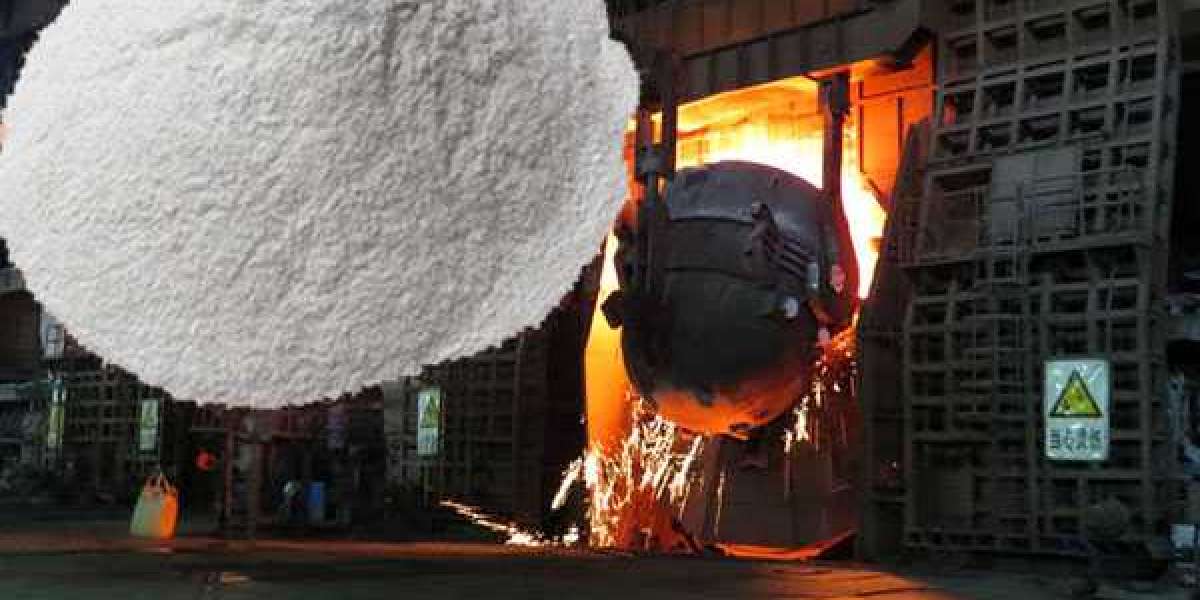
AdTech aluminium refining fluxes have two kinds of granule and powder agent, its main component is chloride salt and other compounds. After proper heating and sieving, the particle size is uniform, which is conducive to uniformly entering the lower layer of the aluminum liquid under the action of the carrier gas in the refining tank. Physical and chemical changes form numerous small bubbles in the molten aluminum and fully contact the molten aluminum to separate H and other harmful gases. And it has good fluidity, and dross and degass molten aluminum.
AdTech fluxes refining process is cost-effective. It is a good performance for separating slag from molten aluminum, and only a small amount of addition is almost no pollution. When it undergoes physical and chemical reactions, it has obvious heat dissipation. This is why the cost is so low.
Aluminum casting is the process of mixing, stirring, standing, refining, slagging, into aluminum ingots, bars, or other products. Aluminum and aluminum alloys will experience varying degrees of loss due to oxidation, refining, slagging and other reasons during the melting and casting process.
The fluxes are suitable for covering, degassing and slag removal in cast aluminum applications. They reduce oxide formation and furnace wall slag, help remove non-metallic inclusions in molten aluminum, reduce the aluminum content in scum, and assist in removing scum.
Compared with powder flux, granular flux products are dust-free and more efficient, with a small amount of addition.
The slag cleaning flux is designed to remove non-metallic inclusions in the molten metal by trapping floating oxide particles.
The covering flux and the dross removing flux can generate a molten layer to protect the metal from oxidation and hydrogen absorption. They gather oxides and non-metallic materials in the molten metal, clean the metal and form good metal-free dross, which can be easily removed.